Our lab investigates the following key areas:
1.The impact of transposons on reshaping the genome of newly formed allopolyploid species: Allopolyploidy is a type of polyploidy that arises from the hybridization of two different species. We investigate how TEs contribute to the rapid genome restructuring that occurs following allopolyploidization.
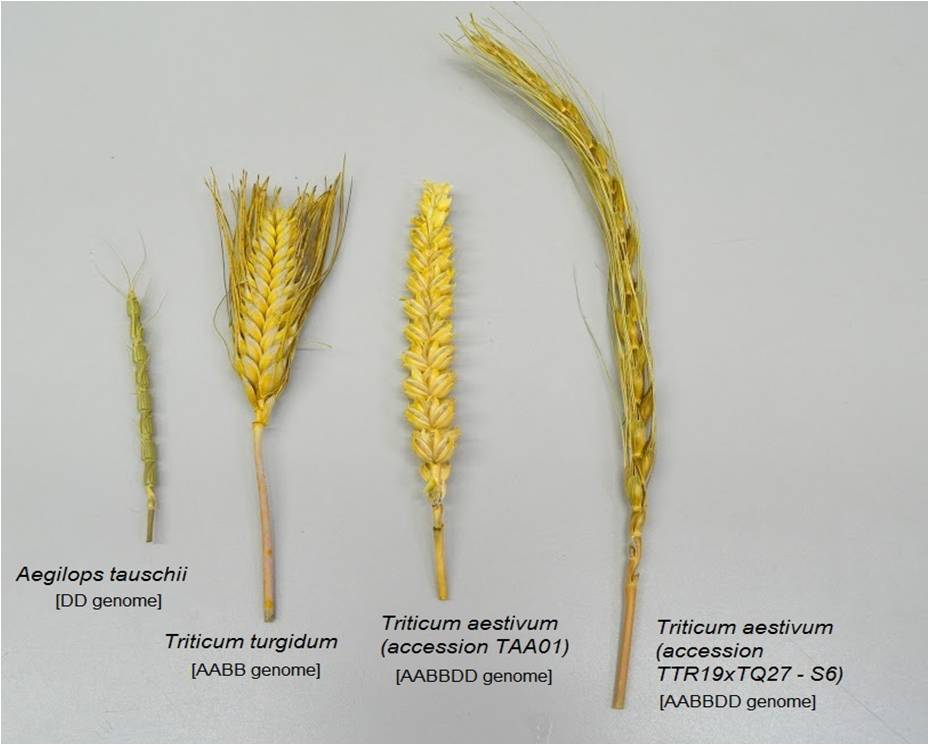

2.The impact of transposons on reshaping the genome of newly formed allopolyploid species: Allopolyploidy is a type of polyploidy that arises from the hybridization of two different species. We investigate how TEs contribute to the rapid genome restructuring that occurs following allopolyploidization.
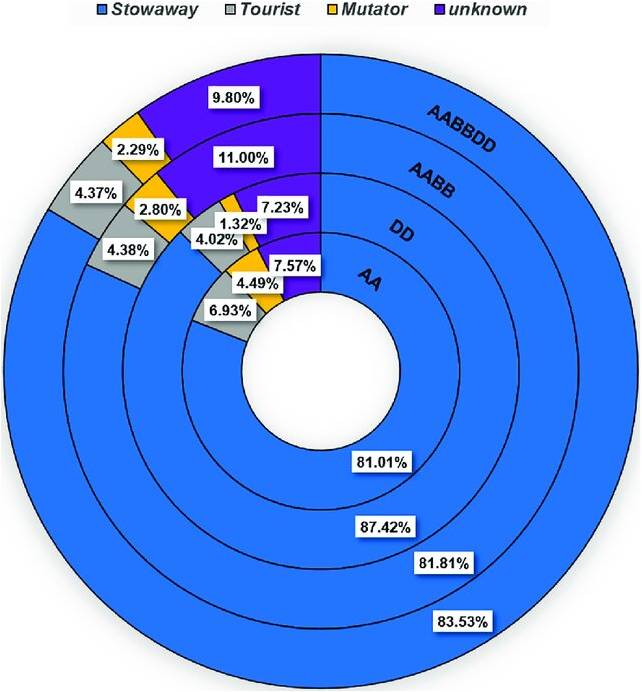
Tritcum and Aegilops genomes. From outer to inner
circls: T. aestivum (AABBDD), T. turdigum ssp
dicoccoides (AABB), Ae. tauschii (DD) and
T. urartu (AA). Percentags denote the fraction of each superfamily from the total number of MITE insertions.
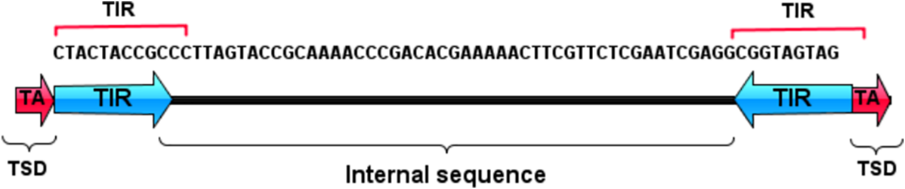
3.The impact of transposons on structural variations in wheat:
TEs can cause large-scale rearrangements in the wheat genome, leading to the creation of new genes, the loss of existing genes, and changes in gene regulation. Our team is studying the underlying mechanisms, and how these structural variations contribute to the diversity and adaptability of wheat.
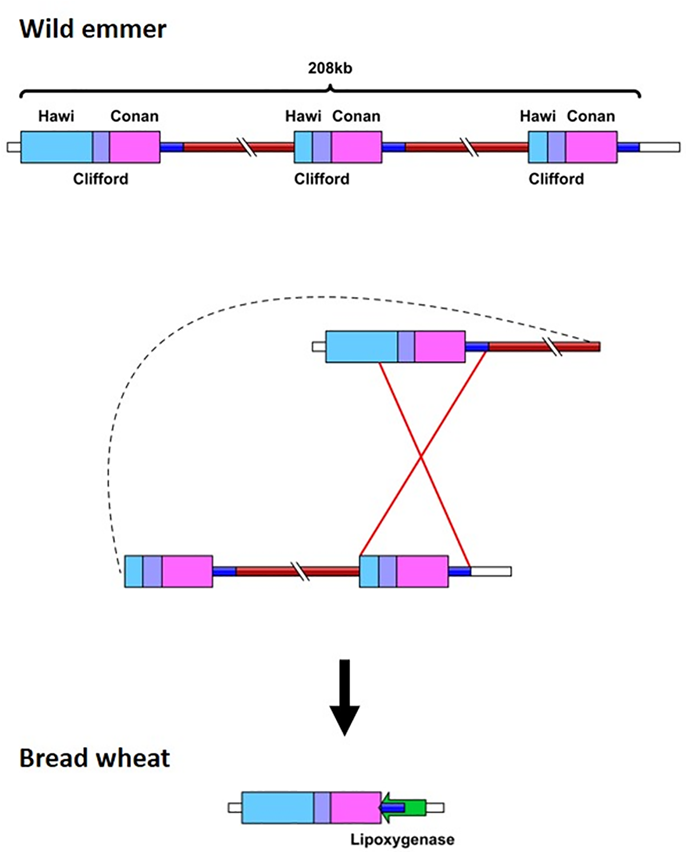
4.The impact of transposons on gene structure and expression variations in wheat:
We found that more than one third of the wheat genes harbor at least one TE element within their sequence (in exon and/or intron sequences). Those insertions might have a direct impact on gene expression. We use RNA-Seq assay to analyze gene expression in the three wheat subgenomes (A, B, and D). In addition, we investigate how TE insertions contribute to the variation in gene expression among different commercial bread wheat varieties.

5.Transposon dynamics in natural populations of wild emmer wheat:
Wild emmer wheat is the ancestor of cultivated wheat. Studying TEs in wild emmer populations can provide insights into the evolutionary history of wheat and the role of TEs in its adaptation to different environments. We study the contribution of TEs to the genetic and epigenetic variations in wild emmer wheat populations. We use wild emmer accessions collected from different sites in Israel, Turkey, Syria, and Lebanon.